How to store data in MySQL using Draco
Context information stored by the Fiware Context Broker only includes the latest value of entity attributes. Draco is an alternative option to Cygnus for storing the historical data produced via the Context Broker ,. Draco needs to be connected to a store.
Draco is a is an easy to use, powerful, and reliable system to process and distribute data. Internally, Draco is based on Apache NiFi, NiFi is a dataflow system based on the concepts of flow-based programming. It supports powerful and scalable directed graphs of data routing, transformation, and system mediation logic. It was built to automate the flow of data between systems. While the term 'dataflow' is used in a variety of contexts, we use it here to mean the automated and managed flow of information between systems.
In the figure below we can see that the user can issue REST HTTP requests. All operations are sent to the Orion Context Broker to be processed. Draco subscribes to Orion Context Broker, so Draco is notified of any change made to entities stored by Orion and then this data is persisted in one or more databases.
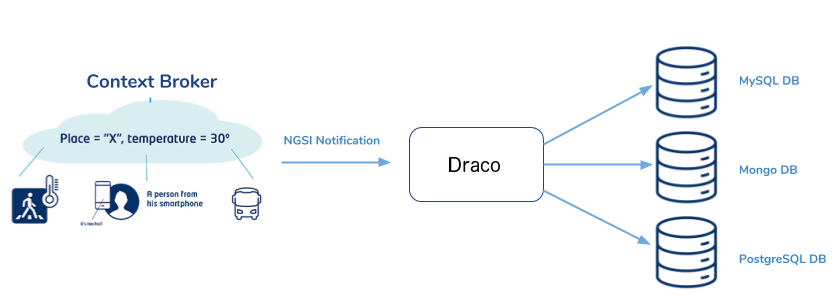
In Draco, you can define where you want to store your data and then, the database and tables will be created with a specific structure defined by the NGSI format. For example, if you want to use the MySQL and Draco, you will have a scenario like is showed in the next figure:
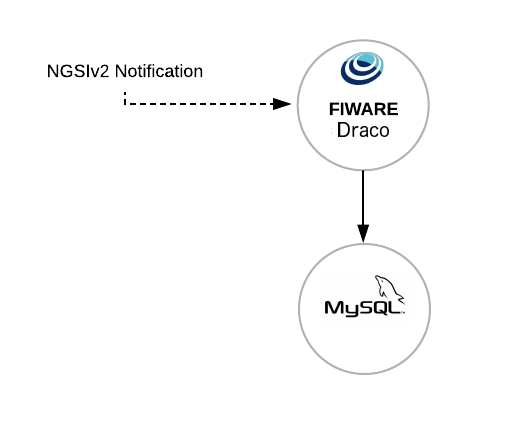
When you start Draco, add and configure your processors, you will be able to persist your data into your database.
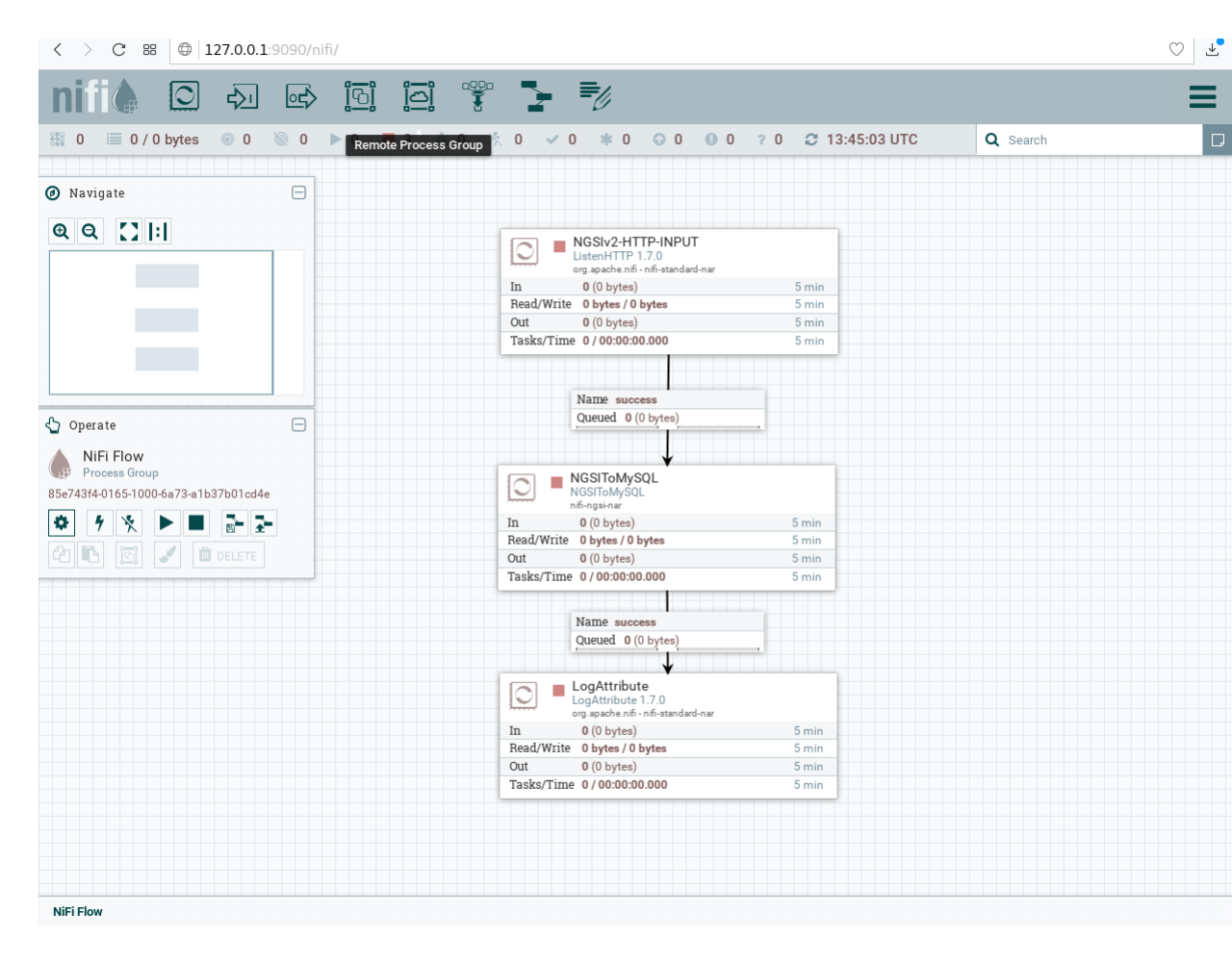
For this case, if Draco receive a notification with this format:
URL=$1
curl $URL -v -s -S --header 'Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8' --header 'Accept: application/json' --header "Fiware-Service: qsg" --header "Fiware-ServicePath: test" -d @- <<EOF
{
"subscriptionId": "51c0ac9ed714fb3b37d7d5a8",
"data": [{
"temperature": {
"type": "Float",
"value": 30.73,
"metadata": {}
},
"type": "Room",
"id": "Room1"
}]
}
EOF
The data will be stored in the MySQL database with the name "qsg" (Fiware-Service value) in the table "test"(Fiware-Service-Path value) and the structure of the table defined by the entities and attributes (for information about the structures please go to the Draco Documentation):
output:
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| mysql |
| performance_schema |
| qsg |
| sys |
+--------------------+
5 rows in set (0.06 sec)
mysql> use qsg;
mysql> show tables;
output:
+---------------+
| Tables_in_qsg |
+---------------+
| test |
+---------------+
1 row in set (0.09 sec)
mysql> select * from test;
output:
+---------------+---------------------+-------------------+----------+------------+-------------+----------+-----------+--------+
| recvTimeTs | recvTime | fiwareServicePath | entityId | entityType | attrName | attrType | attrValue | attrMd |
+---------------+---------------------+-------------------+----------+------------+-------------+----------+-----------+--------+
| 1535550393717 | 08/29/2018 13:46:33 | test | Room1 | Room | temperature | Float | 30.73 | [] |
+---------------+---------------------+-------------------+----------+------------+-------------+----------+-----------+--------+
1 row in set (0.05 sec)
Thus, using Draco Generic enabler you can store all the data coming from the Orion context Broker and the databases and tables will be created automatically.